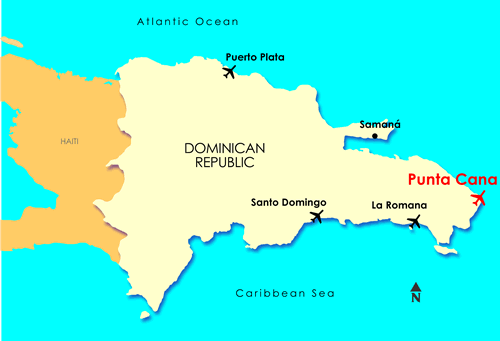
About The Dominican-Republic
The Dominican Republic has the ninth largest economy in Latin America and is the largest economy in the Caribbean and Central American region. Christopher Columbus landed on the island on December 5, 1492, which the Taíno people had inhabited since the 7th century. It became the site of the first permanent European settlement in the Americas; namely Santo Domingo, the oldest continuously inhabited city and the first seat of the Spanish colonial rule in the New World. After three centuries of Spanish rule, with French and Haitian interludes, the Dominican Republic became independent in 1821. The ruler, José Núñez de Cáceres, intended that the Dominican Republic be part of the nation of Gran Colombia, but he was quickly removed by the Haitian government and Dominican slave revolts. Though long known for agriculture and mining, the economy is now dominated by services. The Dominican Republic's economic progress is exemplified by its advanced telecommunication system and transportation infrastructure. The Dominican Republic is the most visited destination in the Caribbean. The year-round golf courses are among the top attractions on the island. A geographically diverse nation, the Dominican Republic is home to the region's tallest mountain peak, Pico Duarte, as well as the Caribbean's largest lake and lowest elevation, Lake Enriquillo. The country is also the site of the first cathedral, castle, monastery, and fortress built in all of the Americas, located in Santo Domingo's Colonial Zone, an area declared as a World Heritage Site byUNESCO. Music and sport are of great importance in the Dominican culture, with Merengue and Bachata as the national dance and music, and baseball as the favorite sport.
Official Languages: Spanish
Population: 10.4 million
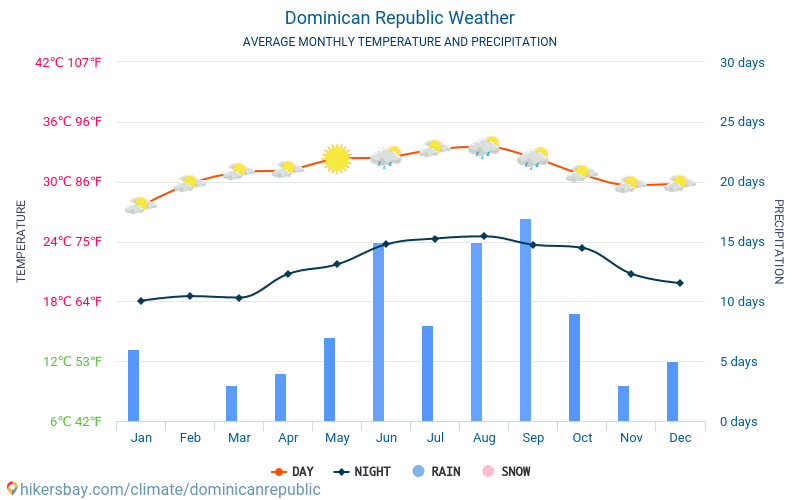
Climate
Culture

Currency

The Dominican peso (DOP, or RD$) is the national currency, with the United States dollar (USD), the Euro (EUR), the Canadian dollar (CAD) and the Swiss franc (CHF) also accepted at most tourist sites. The exchange rate to the U.S. dollar, liberalized by 1985, stood at 2.70 pesos per dollar in August 1986, 14.00 pesos in 1993, and 16.00 pesos in 2000. As of September 2018 the rate was 50.08 pesos per dollar.
Foreign relations

The Dominican Republic has a close relationship with the United States and with the other states of the Inter-American system. The Dominican Republic has very strong ties and relations with Puerto Rico. The Dominican Republic's relationship with neighbouring Haiti is strained over mass Haitian migration to the Dominican Republic, with citizens of the Dominican Republic blaming the Haitians for increased crime and other social problems. The Dominican Republic is a regular member of the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie. The Dominican Republic has a Free Trade Agreement with the United States, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Nicaragua via the Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement. And an Economic Partnership Agreement with the European Union and the Caribbean Community via the Caribbean Forum.
Economy

Emigration
Today, emigration from the Dominican Republic remains high. In 2012 there were approximately 1.7 million people of Dominican descent in the US, counting both native- and foreign-born. There is also a growing Dominican immigration to Puerto Rico, with nearly 70,000 Dominicans living there as of 2010.
Government
Government of the Dominican Republic takes place in a framework of a representative democracy, whereby the President of the Dominican Republic is both head of state, head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in the two chambers of the National Congress. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
Health
In 2007 the Dominican Republic had a birth rate of 22.91 per 1000 and a death rate of 5.32 per 1000. Youth in the Dominican Republic is the healthiest age group.
Languages
The population of the Dominican Republic is mostly Spanish-speaking. The local variant of Spanish is called Dominican Spanish, which closely resembles other Spanish vernaculars in the Caribbean and the Canarian Spanish. In addition, it has influences from African languages and borrowed words from indigenous Caribbean languages particular to the island of Hispaniola. Schools are based on a Spanish educational model; English and French are mandatory foreign languages in both private and public schools, although the quality of foreign languages teaching is poor. Some private educational institutes provide teaching on other languages, notably Italian, Japanese, and Mandarin.
Tourism
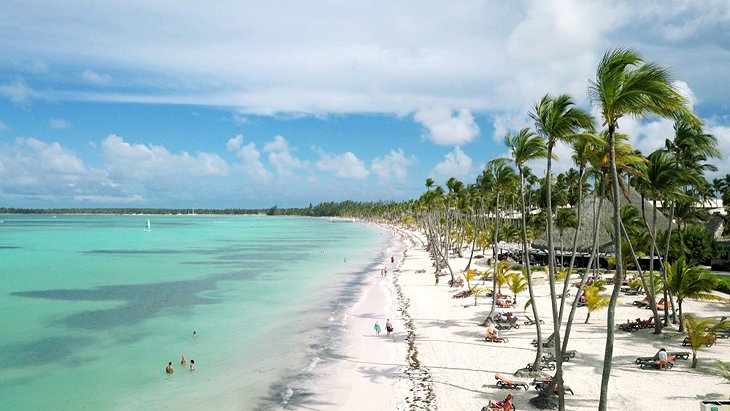

Tourism is one of the fueling factors in the Dominican Republic's economic growth. The Dominican Republic is the most popular tourist destination in the Caribbean. With the construction of projects like Cap Cana, San Souci Port in Santo Domingo, and the Moon Palace Resort in Punta Cana, the Dominican Republic expects increased tourism activity in the upcoming years.
Transport
The Dominican Republic has Latin America's third best transportation infrastructure. The country has three national trunk highways, which connect every major town. In addition to the national highways, the government has embarked on an expansive reconstruction of spur secondary routes, which connect smaller towns to the trunk routes.
Santo Domingo Metro

The Dominican government has put effort towards providing efficient public transportation with the construction of the Santo Domingo Metro, the first mass transit system in the country. The metro is currently the largest in the Caribbean region by length and number of stations.